ایجاد جدول داینامیک با قابلیت صفحه بندی دراندروید
چهارشنبه 14 بهمن 1394در این مقاله قصد داریم یک نمونه پروژه ی آماده یک جدول با اطلاعات که داینامیک هستند و قابلیت صفحه بندی را هم دارند برای شما نمایش دهیم، این نمونه سورس در محیط Android Studio نوشته شده است.
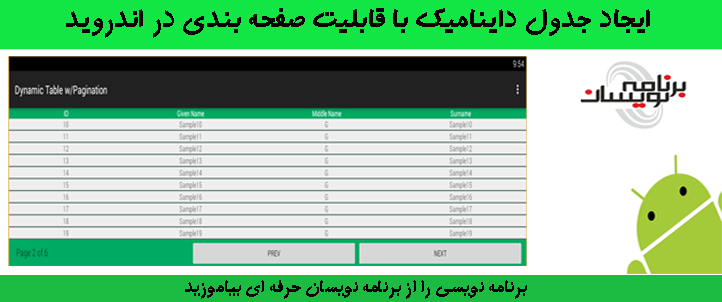
ابتدا داخل لایه ی activity از یک لایه استفاده کرده ایم داخل این لایه یک tablelayout تعریف کرده است، از یک tablerow برای تعریف جدول خود استفاده نمایید و داخل آن از textview برای نمایش اطلاعات استفاده می نماییم، در مرحله ی بعدی یک linearlayout دیگر می اندازید و دکمه و متن برای صفحه بندی را داخل آن تعریف می نماییم.
<ScrollView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/scrollView">
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TableLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/main" >
<TableRow
android:background="#ff00aa63"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/rowHeader">
<TextView
android:text="ID"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:typeface="normal"
android:fontFamily="sans-serif-medium"
android:textColor="@android:color/background_light"
android:id="@+id/tvID"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:text="Given Name"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:typeface="normal"
android:fontFamily="sans-serif-medium"
android:textColor="@android:color/background_light"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
<TextView
android:text="Middle Name"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:typeface="normal"
android:fontFamily="sans-serif-medium"
android:textColor="@android:color/background_light"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
<TextView
android:text="Surname"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:typeface="normal"
android:fontFamily="sans-serif-medium"
android:textColor="@android:color/background_light"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</TableRow>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:background="@drawable/radius_middle"
android:layout_height="2dp" />
</TableLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="#ff00aa63"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Page 1 of 50"
android:id="@+id/txtPageCount"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<Button
style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Prev"
android:id="@+id/btnPrevious"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_marginRight="2dp" />
<Button
style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Next"
android:id="@+id/btnNext"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_marginLeft="2dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
حالا تعریف کلاس ها است یک کلاس به نام person تعریف نمایید و با استفاده از get , set اطلاعات را می گیرد و نمایش می دهد.
public class Person {
private Integer _id;
private String _givenName;
private String _middleName;
private String _surName;
public Person(Integer _id, String _givenName, String _middleName, String _surName) {
this._id = _id;
this._givenName = _givenName;
this._middleName = _middleName;
this._surName = _surName;
}
public Integer get_id() {
return _id;
}
public void set_id(Integer _id) {
this._id = _id;
}
public String get_givenName() {
return _givenName;
}
public void set_givenName(String _givenName) {
this._givenName = _givenName;
}
public String get_middleName() {
return _middleName;
}
public void set_middleName(String _middleName) {
this._middleName = _middleName;
}
public String get_surName() {
return _surName;
}
public void set_surName(String _surName) {
this._surName = _surName;
}
}
کلاس بعدی کلاس برای صفحه بندی کردن صفحات جدول مان است که یک مقدار پیش فرض بگیرد و داخل این کلاس صفحه ی شروع و پایان و تعداد صفحات و max تعداد صفحات و ... نمایش می دهد.
public class Pageable<T> {
/** the default page size */
public static final int DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE = 10;
private static final int PAGE_WINDOW = 10;
/** the list over which this class is paging */
private List<T> list;
/** the page size */
private int pageSize = DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE;
/** the current page */
private int page;
/** the starting index */
private int startingIndex;
/** the ending index */
private int endingIndex;
/** the maximum number of pages */
private int maxPages;
/**
* Creates a new instance with the specified list.
*
* @param list a List
*/
public Pageable(List<T> list) {
this.list = list;
this.page = 1;
this.maxPages = 1;
calculatePages();
}
private void calculatePages() {
if (pageSize > 0) {
// calculate how many pages there are
if (list.size() % pageSize == 0) {
maxPages = list.size() / pageSize;
} else {
maxPages = (list.size() / pageSize) + 1;
}
}
}
/**
* Gets the list that this instance is paging over.
*
* @return a List
*/
public List<T> getList() {
return this.list;
}
/**
* Gets the subset of the list for the current page.
*
* @return a List
*/
public List<T> getListForPage() {
return list.subList(startingIndex, endingIndex);
}
/**
* Gets the page size.
*
* @return the page size as an int
*/
public int getPageSize() {
return this.pageSize;
}
/**
* Sets the page size.
*
* @param pageSize the page size as an int
*/
public void setPageSize(int pageSize) {
this.pageSize = pageSize;
calculatePages();
}
/**
* Gets the page.
*
* @return the page as an int
*/
public int getPage() {
return this.page;
}
/**
* Sets the page size.
*
* @param p the page as an int
*/
public void setPage(int p) {
if (p >= maxPages) {
this.page = maxPages;
} else if (p <= 1) {
this.page = 1;
} else {
this.page = p;
}
// now work out where the sub-list should start and end
startingIndex = pageSize * (page-1);
if (startingIndex < 0) {
startingIndex = 0;
}
endingIndex = startingIndex + pageSize;
if (endingIndex > list.size()) {
endingIndex = list.size();
}
}
/**
* Gets the maximum number of pages.
*
* @return the maximum number of pages as an int
*/
public int getMaxPages() {
return this.maxPages;
}
/**
* Determines whether there is a previous page and gets the page number.
*
* @return the previous page number, or zero
*/
public int getPreviousPage() {
if (page > 1) {
return page-1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
/**
* Determines whether there is a next page and gets the page number.
*
* @return the next page number, or 0
*/
public int getNextPage() {
if (page < maxPages) {
return page+1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
/**
* Gets the minimum page in the window.
*
* @return the page number
*/
public int getMinPageRange() {
if (getPage() > PAGE_WINDOW) {
return getPage() - PAGE_WINDOW;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
/**
* Gets the maximum page in the window.
*
* @return the page number
*/
public int getMaxPageRange() {
if (getPage() < (getMaxPages() - PAGE_WINDOW)) {
return getPage() + PAGE_WINDOW;
} else {
return getMaxPages();
}
}
}
در مرحله ی آخر تعریف ابزار های مورد استفاده و مشخص کردن id مورد نظر برای آن ها است، علاوه بر آن دکمه های استفاده شده در صفحه را تعریف می نماید و برای هر کدام رویداد مربوط به خودشان را می نویسید. و یک رویداد هم برای نمایش جدول استفاده می کند که هر کدام از مقادیری را که در کلاس person تعریف کرده است داخل textview مورد نظر قرار می دهد.
import android.content.res.Resources;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.support.v7.app.ActionBarActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TableLayout;
import android.widget.TableRow;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity {
TableLayout maintable;
TableRow tableRow,rowHead;
LinearLayout separator;
TextView value;
TextView textView;
Pageable<Person> pageableArray;
Button buttonNext;
Button buttonPrev;
TextView textViewPageCount;
ArrayList<Person> myValues;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tvID);
maintable = (TableLayout) findViewById(R.id.main);
rowHead = (TableRow) findViewById(R.id.rowHeader);
buttonNext = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnNext);
buttonPrev = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnPrevious);
textViewPageCount = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.txtPageCount);
myValues = new ArrayList<>();
buttonNext.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
pageableArray.setPage(pageableArray.getNextPage());
tableRow.removeAllViews();
displayPage();
textViewPageCount.setText("Page " + pageableArray.getPage() + " of " + pageableArray.getMaxPages());
}
});
buttonPrev.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
pageableArray.setPage(pageableArray.getPreviousPage());
tableRow.removeAllViews();
displayPage();
textViewPageCount.setText("Page " + pageableArray.getPage() + " of " + pageableArray.getMaxPages());
}
});
for(int i=0; i<= 55; i++){
myValues.add(new Person(i,"Sample" + i,"G","Sample" + i));
}
pageableArray = new Pageable<>(myValues);
pageableArray.setPageSize(10);
pageableArray.setPage(1);
textViewPageCount.setText("Page " + pageableArray.getPage() + " of " + pageableArray.getMaxPages());
displayPage();
}
public void displayPage() {
maintable.removeAllViews();
maintable.addView(rowHead);
for (Person v : pageableArray.getListForPage()) {
tableRow = new TableRow(this);
tableRow.setLayoutParams(new TableLayout.LayoutParams(TableLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, TableLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
value = new TextView(this);
value.setLayoutParams(textView.getLayoutParams());
value.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL);
value.setText(String.valueOf(v.get_id()));
tableRow.addView(value);
value = new TextView(this);
value.setLayoutParams(textView.getLayoutParams());
value.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL);
value.setText(v.get_givenName());
tableRow.addView(value);
value = new TextView(this);
value.setLayoutParams(textView.getLayoutParams());
value.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL);
value.setText(v.get_middleName());
tableRow.addView(value);
value = new TextView(this);
value.setLayoutParams(textView.getLayoutParams());
value.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL);
value.setText(v.get_surName());
tableRow.addView(value);
maintable.addView(tableRow);
addSeparator();
}
}
private void addSeparator() {
Resources res = MainActivity.this.getResources();
separator = new LinearLayout(MainActivity.this);
separator.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
separator.setLayoutParams(new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, 2));
separator.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor("#5e7974"));
separator.setDividerDrawable(res.getDrawable(R.drawable.radius_middle));
maintable.addView(separator);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will
// automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long
// as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml.
int id = item.getItemId();
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
if (id == R.id.action_settings) {
return true;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
داخل کد بالا از یک منو هم استفاه شده است می توانید منو را داخل صفحه در صورت نیاز قرار دهید.
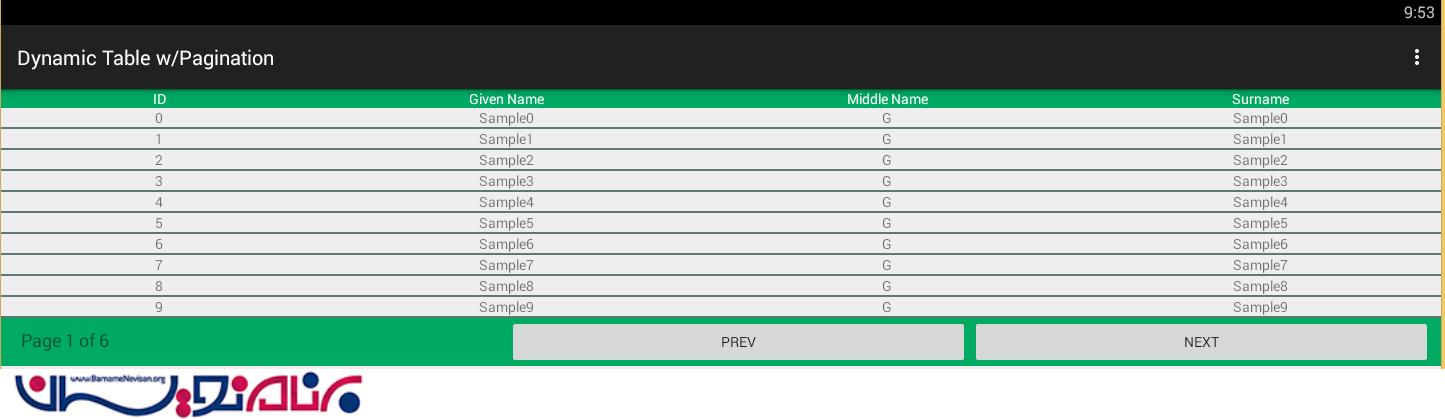
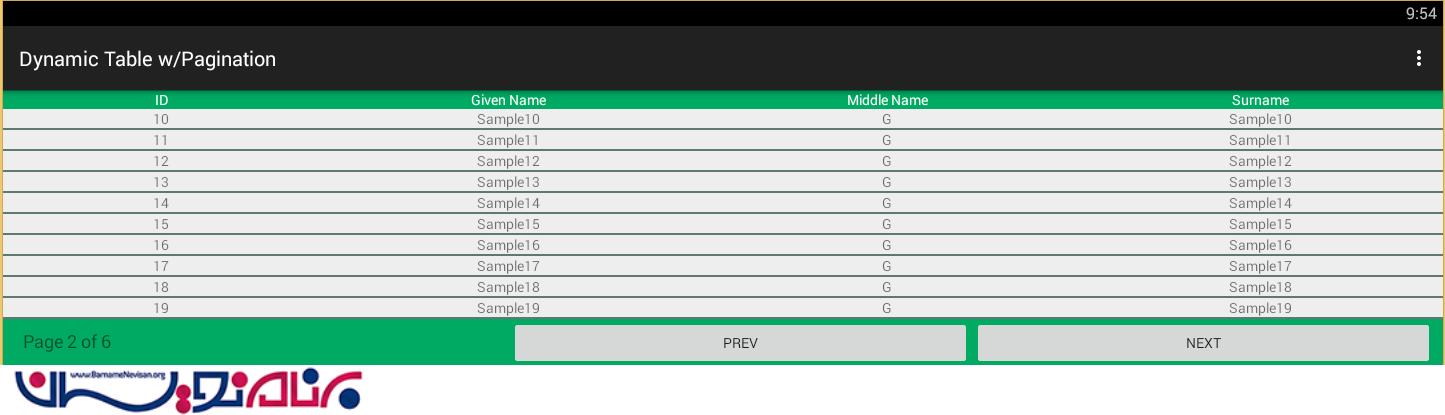
در نهایت خروجی به صورت زیر خواهد بود:
- Android
- 3k بازدید
- 5 تشکر
